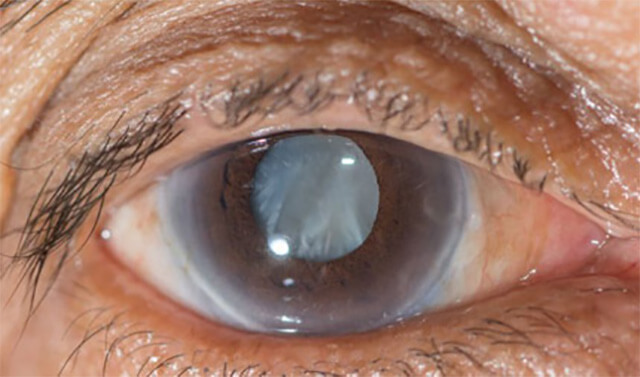
CATARACT
A cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye which leads to a decrease in vision. A cataract begins when protein in the eye forms clumps that prevent the lens from sending clear images to the retina. The retina works by converting the light that comes through the lens into signals. It sends the signals to the optic nerve, which carries them to the brain. A cataract develops slowly and eventually interferes with your vision.
You might end up with cataracts in both eyes, but they usually don’t form at the same time. Cataracts are common in older people.
A cataract is the commonest cause of severe visual impairment and blindness being responsible for 45.3% and 43.0% respectively.
SYMPTOMS OF CATARACT
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF CATARACT INCLUDE:
- Blurry vision.
- Trouble seeing at night.
- Increased sensitivity to glare.
- Seeing colors as faded.
- Halos surrounding light.
- Double vision in the affected eye.
A need for frequent changes in prescription glasses.
CAUSES OF CATARACT
COMMON CAUSES OF CATARACT INCLUDE:
- Age.
- Trauma.
- Smoking and Alcohol.
- Radiation Therapy.
- The long-term use of steroids and other medications.
- Ultraviolet Radiation.
TYPES OF CATARACT
There are different types of cataracts. They are classified based on where and how they develop in your eye.
- Nuclear cataracts form in the middle of the lens and cause the nucleus, or the center, to become yellow or brown.
- Cortical Cataracts are wedge-shaped and form around the edges of the nucleus.
- Posterior Capsular cataracts form faster than the other two types and affect the back of the lens.
- Congenital Cataract, which is present at birth or form during a baby’s first year, are less common than age-related cataracts.
- Secondary Cataracts are caused by disease or medication.
- Diseases that are linked with the development of cataracts include glaucoma and diabetes. The use of steroid prednisone and other medications can sometimes lead to cataracts.
- Traumatic Cataracts develop after an injury to the eye, but it can take several years for this to happen.
- Radiation Cataracts can form after a person undergoes radiation treatment for cancer.
RISK FACTORS OF CATARACTS
Risk factors associated with cataract include:
- Older age.
- Heavy alcohol use.
- Smoking.
- Obesity.
- High blood pressure.
- Previous eye injuries.
- A family history of cataracts.
- Too much sun exposure.
- Diabetes.
- Exposure to radiation from X-rays and cancer treatment.
PREVENTION OF CATARACT
To reduce your risk of developing Cataract:
- Protect your eyes from UVB rays by wearing sunglasses outside.
- Have regular eye exams.
- Stop smoking.
- Eat fruits and vegetables that contain antioxidants.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Keep diabetes and other medical conditions in check.
TREATMENT OF CATARACT
If you are unable to undergo surgery, your doctor may be able to help you manage your symptoms. They may suggest stronger eyeglasses or sunglasses with an anti-glare coating.
SURGERY
Surgery is recommended when a cataract prevents you from going about your daily activities, such as reading or driving. It is also performed when cataracts interfere with the treatment of other eye problems.
• One surgical method, known as Phacoemulsification, involves the use of ultrasound waves to break the lens apart and remove the pieces.
• Extracapsular surgery involves removing the cloudy part of the lens through a long incision in the cornea. After surgery, an artificial intraocular lens is placed where the natural lens was.
Surgery to remove a cataract is generally very safe and has a high success rate. Most people can go home the same day as their surgery.