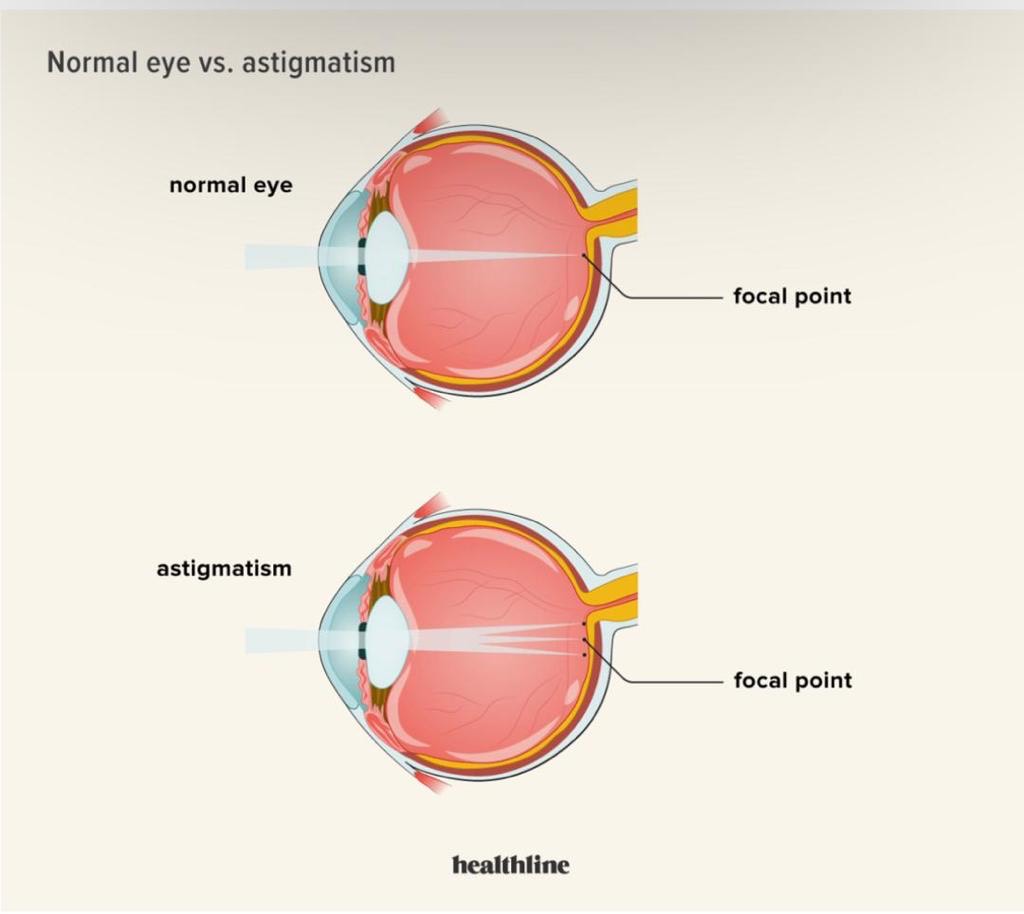
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error, which occurs when there is an unusual curvature in the eye’s lens or cornea, this prevents light from being focused in the focal point of the retina. In a person with astigmatism, the cornea is often egg- or football-shaped and curves differently from top to bottom than it does from side to side, rather than being perfectly round. As a result of this, the light will focus on two points on the retina instead of one. This results to decreased, blurry and distorted vision.


The pictures above differentiates what the normal eye and an astigmatic eye sees.
WHAT CAUSES ASTIGMATISM?
It’s not known what causes astigmatism, but genetics is a big factor. It’s often present at birth, but it may develop later in life. It may also occur as a result of an injury to the eye or after eye surgery. Astigmatism often occurs with nearsightedness or farsightedness.
Sometimes, a rare condition called keratoconus causes astigmatism. This eye disease affects the cornea, causing the clear tissue on the cornea to thin and bulge out. This leads to cloudy or blurry vision, and sensitivity to bright lights. The cause of keratoconus is also unknown, but it’s believed to be hereditary, too.
Keep in mind that while reading with low or dim lights can make it harder for eyes to focus, it doesn’t harm vision or cause astigmatism. However, if you already have an eye with astigmatism, and you read in low light, you might notice increased blurriness.
SYMPTOMS OF ASTIGMATISM
The primary symptoms of astigmatism include:
- Blurry, distorted, or fuzzy vision at all distances (up close and far away)
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Eyestrain
- Squinting
- Frontal headache.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Miscalling of letters.
TREATMENT
- Corrective lenses:
Corrective lenses can help correctly project images onto the retina. These may be in the form of glasses or contact lenses.
Lenses for astigmatism will need:
- A spherical power, to correct the near or far-sightedness
- A Cylinder lens power, to correct the astigmatism
- An axis designation that describes the positioning of the astigmatism
- If a person has presbyopia, their lenses will require additional, or add, power to treat this.
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K):
Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) is a treatment that uses rigid contact lenses to temporarily correct the irregular curvature of your cornea. You’ll wear rigid contact lenses for limited periods of time. You may wear them during sleep and then remove them during the day.
This does not permanently improve vision, your vision will be clear few hours after you remove it. The benefits of Ortho-K are only present when using it. Your vision will return to its previous state after stopping Ortho-K.
- Refractive surgery:
Your doctor may recommend refractive surgery . The surgery treats astigmatism by reshaping your cornea. Refractive surgery improves vision and reduces the need for eyeglasses or contact lenses. An eye surgeon uses a laser beam to reshape the curves of the cornea, which corrects the refractive error. Before surgery, doctors will evaluate you and determine if you’re a good candidate for the surgery.
The goal of treating astigmatism is to improve vision clarity and eye comfort.
How is it diagnosed?
Astigmatism is diagnosed with an eye examination. A complete eye examination involves both a series of tests to check eye health and the refractive state of your eyes.
